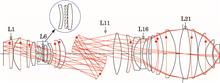
We have proposed and developed a design method of a freeform surfaces (FFSs) based hyper-numerical-aperture deep ultraviolet (DUV) projection objective (PO) with low aberration. With an aspheric initial configuration, lens-form parameters were used to determine the best position to remove elements and insert FFSs. The designed FFSs PO reduced two elements without increasing the total thickness of the glass materials. Compared with aspheric initial configuration, the wavefront error of the FFSs PO decreased from 0.006λ to 0.005λ, the distortion reduced from 1 to 0.5 nm, and the aspheric departure decreased from 1.7 to 1.35 mm. The results show that the design method of the FFSs PO is efficient and has improved the imaging performance of PO. The design method of FFSs PO provides potential solutions for DUV lithography with low aberrations at 10–5 nm nodes.
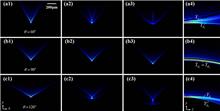
We numerically and experimentally investigate the propagation of deformed 2D vortex Airy beams. Our results show that, for different topological charges, two parabolic trajectories that can be controlled by changing the initial wing angle always dominate the beam propagations. In this case, the main lobes take different propagation distances to restore to the peak intensity. The profiles tend to evolve into 1D or 2D Airy-like patterns to various degrees in the same propagation distance. Furthermore, the whole profiles yield a small change in their acceleration direction, depending on the topological charge and the initial wing angle.
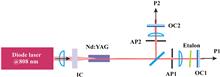
We report efficient power scaling of the laser output with an adaptive beam profile from an Nd:YAG dual-cavity master oscillator using a three-stage end-pumped Nd:YVO4 amplifier. We succeed in the fast switching of an excited laser mode by modulating an acousto-optic modulator loss in a dual-cavity master oscillator, thereby achieving temporal modulation of the output beam profile. The outputs from the master oscillator are amplified via a three-stage power amplifier yielding 36.6, 40.5, and 45.4 W of the maximum output at 116.8 W of incident pump power for the transverse electromagnetic, Laguerre–Gaussian, and quasi-top-hat beam, respectively. The prospects for further power scaling and applications via the dual-cavity master-oscillator power-amplifier (MOPA) system are considered.
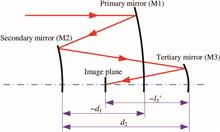
In this Letter, a novel and compact freeform off-axis three-mirror imaging system and its detailed design method are proposed. The primary mirror and tertiary mirror of the system have the same surface analytical expression and they are integrated on one single freeform surface. In this way, the alignment process is made much easier due to the much fewer degrees of freedom. In addition, the difficulty and cost for the data handling, fabrication, and testing of the freeform surfaces and system can also be significantly reduced in some cases, especially compared with the configuration having multiple surfaces of different expressions integrated on one monolithic substrate. The final system has a 100 mm effective focal length and a 4°×3° field of view. The modulation transfer function of the system is close to the diffraction-limit.
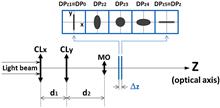
We propose a novel small-angle measuring optical method based on the astigmatic effect of two orthogonally placed cylindrical lenses. According to the one-to-one correspondence between the laser spot shape and the angle, the angle is determined. We theoretically analyze the measuring range and demonstrate that a longer distance between the rotating axis and the optical axis leads to a smaller measuring range, but better sensitivity. Also, an associated experimental system is established and a measuring range of 0.94 mrad (cubic fit r=0.9993) as well as a good linear range of 0.37 mrad (linear fit r=0.9994) with a resolution of 8 μrad is achieved.
In this Letter, we propose a novel configuration and design method of freeform, dual fields-of-view (FOVs), dual focal lengths, off-axis three-mirror zoom imaging systems. The switch of the two zooms is achieved by rotating a single mirror element. The design of a freeform, dual focal lengths zoom system is realized by a point-by-point design approach for the first time to our knowledge. This method enables the direct design of freeform surfaces from initial planes using given system specifications and configuration, and the designed system can be taken as a good starting point for further optimization. A freeform, dual FOVs, dual focal lengths, off-axis three-mirror zoom system is demonstrated. The F-numbers of the two zooms are 2 and 2.4. The dual FOVs are 3°×3° and 2.5°×2.5°. After final optimization, both of the zooms achieve high performances.
Theoretical analysis of the electromagnetic field distribution in the focal region of a long metallic parabolic reflector that has its surface covered with a magnetized plasma layer is derived. The incident wave is considered to be with a general oblique incidence for both parallel and perpendicular polarizations. The electromagnetic field intensity expressions along the focal region are obtained accurately using Maslov’s method. The effects of plasma thickness on the reflected and transmitted field distributions are investigated. The effects of other physical parameters such as the angle of incidence and the plasma and cyclotron frequencies on the transmitted field-intensity distribution along the focal region are also studied. The results obtained by Maslov’s method and Kirchhoff’s approximation are found to be in a good agreement.
In this Letter, a new fractional entangling transformation (FrET) is proposed, which is generated in the entangled state representation by a unitary operator exp{iθ(ab +a b)} where a(b) is the Bosonic annihilate operator. The operator is actually an entangled one in quantum optics and differs evidently from the separable operator, exp{iθ(a a+b b)}, of complex fractional Fourier transformation. The additivity property is proved by employing the entangled state representation and quantum mechanical version of the FrET. As an application, the FrET of a two-mode number state is derived directly by using the quantum version of the FrET, which is related to Hermite polynomials.
We propose an LED reshaping lens design for a handheld underwater wireless optical system to solve the problem of targeting the receiver. The simulation results shows that the designed lens can achieve 0.91 light intensity uniformity and 91.39% optical efficiency in hemisphere space, even with the actual LED model. After fabrication with computer numeric control, the work demonstrates the design to be effective.
In order to detect the aberration from a wide field of view (FOV) on the retina with adaptive optics, we present a multiple-object Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor (MOSHWFS) design. The simulated results indicate that the wavefront from our MOSHWFS can be reconstructed for multiple objects, and the measurement error can be less than λ/7 with an MOSHWFS with an FOV of 6.7°, for maximum eye aberration. The experimental result with two objects indicates that the measurement error can be less than λ/14, with the root mean square of the reference wavefront as 0.798λ and 0.895λ, respectively.
Analysis of glass homogeneity using the attaching interferometric data model neglects body distribution. To improve analysis accuracy, we establish the three-dimensional gradient index (GRIN) model of glass index by analyzing fused silica homogeneity distribution in two perpendicular measurement directions. Using the GRIN model, a lithography projection lens with a numerical aperture of 0.75 is analyzed. Root mean square wavefront aberration deteriorates from 0.9 to 9.65 nm and then improves to 5.9 nm after clocking.
Higher-band self-trapping and oscillation (rotation) of nonlinear quadruple beams in two-dimensional (2D) square photonic lattices are numerically demonstrated. Under appropriate conditions of nonlinearity, a quadruple-like beam can self-trap into localized modes that reside in the second Bragg reflection gap through single-site excitation. By changing the initial orientation of the incident quadruple beam related to the lattices, periodic oscillations of the localized quadruple mode may be obtained. The localized quadruple state becomes a rotating doubly charged optical vortex (DCV) during rotation and should undergo charge-flipping when the rotating direction is reversed.
The perturbation theory of matrices is applied to ray transfer matrices (RTMs) to describe an optical component with aberration. A quantitative description of the perturbation extent corresponding to aberration strength is provided using condition numbers and absolute errors for the perturbed RTM. An application to a single small aberration is presented, and the results are compared with those of the diffraction theory of aberrations.
We demonstrate the rotating properties of Bragg reflections and spatial lattice solitons in rotating photonic lattices by analyzing the linear and nonlinear propagations of light. It reveals that the Bragg reflection of the light waves rotates synchronously with the lattices, leading to the rotation of the Bloch waves during propagations. In the presence of nonlinearity, rotating lattice solitons from different transmission bands can propagate in a relatively stable manner. However, reduced-symmetry solitons at point X2 cannot easily rotate synchronously with the lattice, owing to Coriolis forces. Moreover, additional angular momenta are added to the off-axis propagating solitons.